C comes with a built-in pseudo-random number generator. It is implemented as two separate functions that live in the cstdlib Header srand lets the initial seed value to a value that is passed in by the caller. Srand should only be called once at the beginning of your program.
- Nov 21, 2010 I have been told that to use srand in C you must use either of the following header files stdlib.h (C) or cstdlib (C) But I noticed that srand still works without me having to include any of those two files. So could somebody tell me exactly what I need them for and why I need them for srand. I know I need to use but I want to know why I need to use stdlib.h (C) or cstdlib (C.
- Feb 12, 2016 Short c code that can be used to simulate multiple rolls of a dice. Simulating the Roll of a Dice With rand and srand Ali Sheikh. Buckys C Programming Tutorials - 9 - Functions.
| Language | ||||
| Standard Library Headers | ||||
| Freestanding and hosted implementations | ||||
| Named requirements | ||||
| Language support library | ||||
| Concepts library(C++20) | ||||
| Diagnostics library | ||||
| Utilities library | ||||
| Strings library | ||||
| Containers library | ||||
| Iterators library | ||||
| Ranges library(C++20) | ||||
| Algorithms library | ||||
| Numerics library | ||||
| Input/output library | ||||
| Localizations library | ||||
| Regular expressions library(C++11) | ||||
| Atomic operations library(C++11) | ||||
| Thread support library(C++11) | ||||
| Filesystem library(C++17) | ||||
| Technical Specifications |
| Common mathematical functions | ||||
| Mathematical special functions(C++17) | ||||
| Mathematical constants(C++20) | ||||
| Floating-point environment(C++11) | ||||
| Complex numbers | ||||
| Numeric arrays | ||||
| Pseudo-random number generation | ||||
| Compile-time rational arithmetic(C++11) | ||||
| Numeric algorithms | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
| Interpolations | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
| Generic numeric operations | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
(C++17) | ||||
| Bit operations | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
(C++20) |
| Uniform random bit generators | ||||
(C++20) | ||||
| Engines and engine adaptors | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Non-deterministic generator | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Distributions | ||||
| Uniform distributions | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Bernoulli distributions | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Poisson distributions | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Normal distributions | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Sampling distributions | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| Seed Sequences | ||||
(C++11) | ||||
| C library |
Defined in header <cstdlib> |
Seeds the pseudo-random number generator used by std::rand() with the value seed.
If rand() is used before any calls to srand(), rand() behaves as if it was seeded with srand(1).
Each time rand() is seeded with the same seed, it must produce the same sequence of values.
srand() is not guaranteed to be thread-safe.
Srand Function In Dev C 2017
Contents |
[edit]Parameters
| seed | - | the seed value |
[edit]Return value
(none)
[edit]Notes
Generally speaking, the pseudo-random number generator should only be seeded once, before any calls to rand(), at the start of the program.It should not be repeatedly seeded, or reseeded every time you wish to generate a new batch of pseudo-random numbers.
C++ Srand Seed
Standard practice is to use the result of a call to time(0) as the seed.However, time() returns a time_t value, and time_t is not guaranteed to be an integral type.In practice, though, every major implementation defines time_t to be an integral type, and this is also what POSIX requires.
[edit]Example
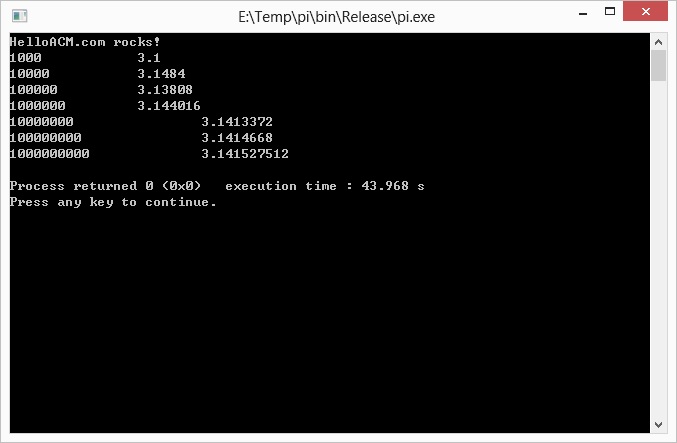
Possible output:
[edit]See also
C++ Srand Time Null
| generates a pseudo-random number (function)[edit] | |
| maximum possible value generated by std::rand (macro constant)[edit] | |
| reseeds the per-thread random engine (function)[edit] | |
C documentation for srand | |